Haemophilia Treatment
This inherited lifelong condition affects the blood clotting factors in some people.
OVERVIEW
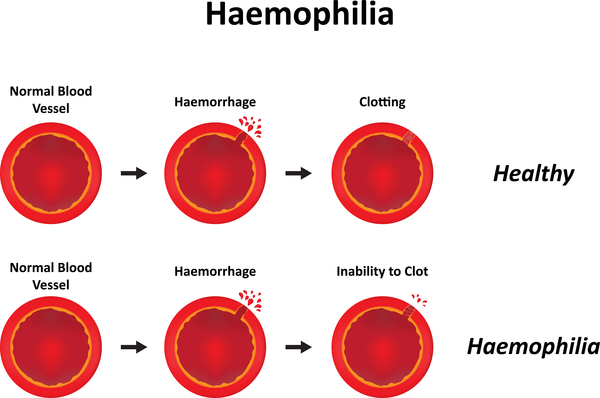
- Haemophilia is a lifelong blood clotting disorder, able to be managed with treatment. It is hereditary (X-linked recessive) and most usually only males suffer the symptoms.
- Haemophilia is caused by lack of activity of blood clotting factors VIII or IX. Symptoms include bruising, internal bleeding at joints and bleeding following surgery and injury.
- 1 in 10,000 men have haemophilia A. 1 in 50,000 men have haemophilia B
- Treatment involves using a replacement blood clotting factor and replacement of lost blood when necessary
- It is a common myth that a sufferer of haemophilia bleeds profusely from even the smallest of cuts, and will bleed to death – the fact is, clotting just takes longer
- Haemophilics may suffer joint pain and deformities in the long-term
- These days clotting products undergo a heat treatment which kills the HIV and Hepatitis B and C viruses, preventing transmission
- Von Willebrand disorder is similar to haemophilia as far as it affects the function of the blood platelets and is inherited, however symptoms affect both males and females
- Most people with haemophilia receiving treatment lead relatively normal lives. Support groups can prove helpful
- When planning a family, the condition can be detected in carrying females, and diagnosis before birth is possible
 Dr. Girish Badarkhe
Dr. Girish Badarkhe